Air Cooled Heat Exchanger
An Air Cooled Heat Exchanger (ACHE) is a mechanical device used to cool fluids such as oil, gas, or water by transferring heat from the fluid to the ambient air. Instead of using water or other liquid cooling media, ACHEs rely solely on air movement, either natural or forced, to achieve thermal regulation.
They are commonly found in industries where water availability is limited or where closed-loop systems are required. These heat exchangers play a critical role in maintaining equipment efficiency, preventing overheating, and ensuring system reliability.
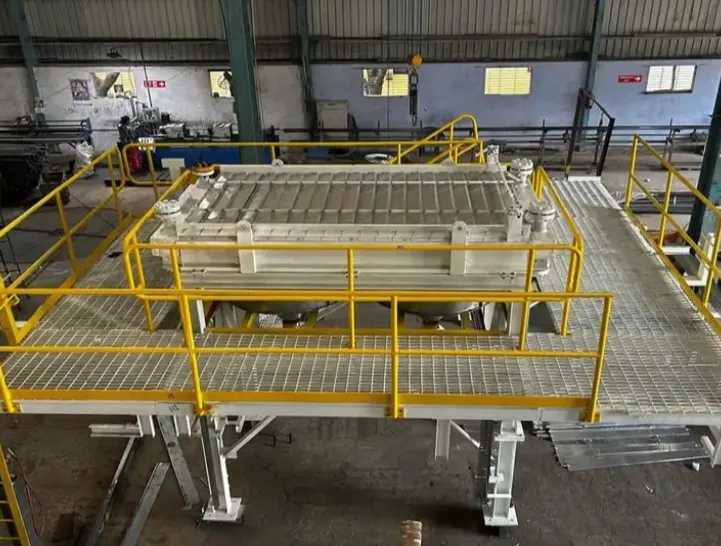

How Does an Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Work?
The basic working principle of an air cooled heat exchanger revolves around heat transfer through convection. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
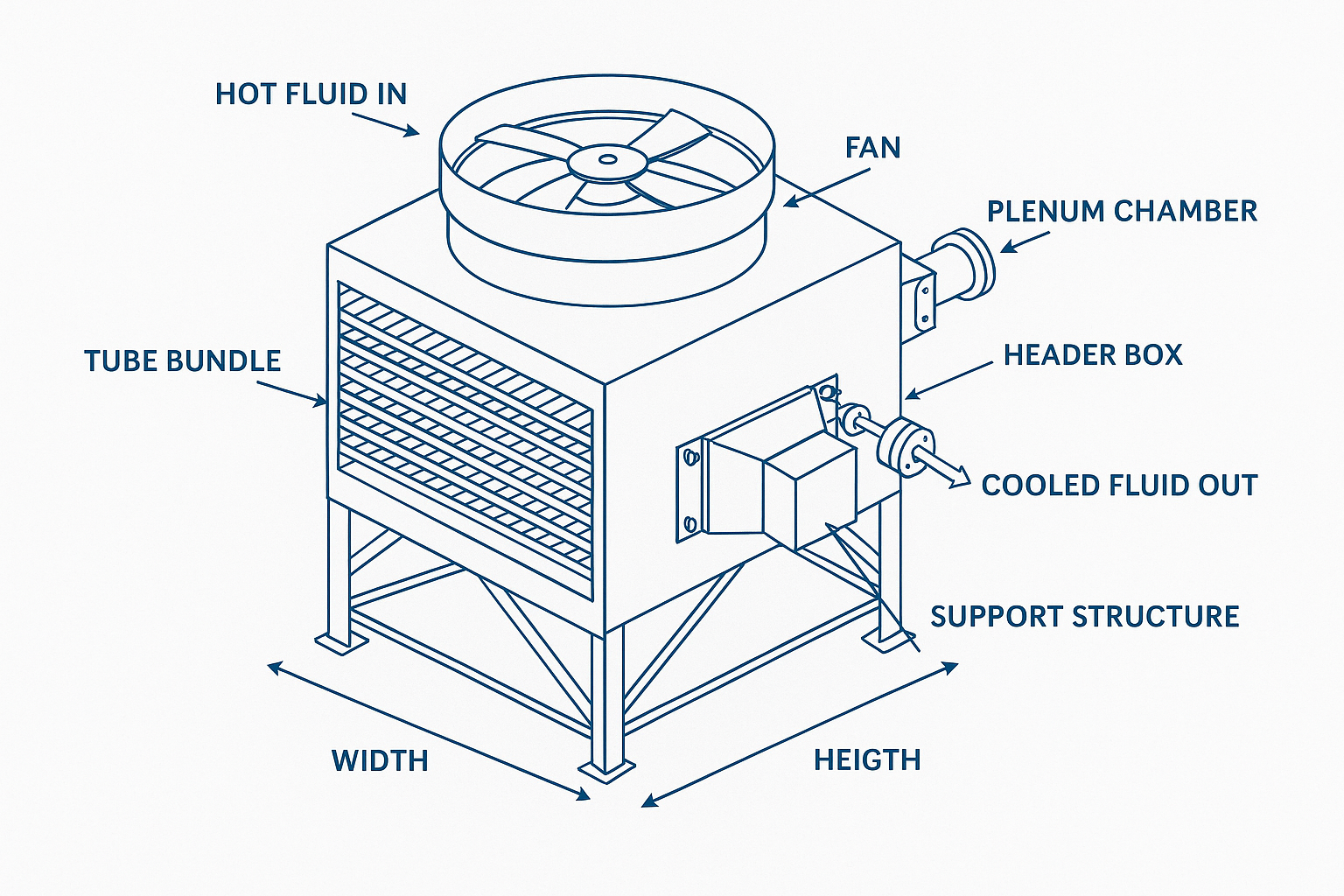
- Hot Fluid Enters Tubes: The process fluid, often hot oil or gas, enters the heat exchanger and flows through a bundle of tubes.
- Heat Transfer Occurs: As air is blown or drawn across these tubes using fans, heat from the fluid is transferred to the surrounding air.
- Cooled Fluid Exits: After passing through the heat exchanger, the now-cooled fluid exits the system and returns to the process cycle.
Fans (usually axial or centrifugal) are used to force air across the tube bundles, increasing the rate of heat dissipation. The combination of finned tubes, fans, and headers allows for efficient air-side heat rejection.
Why Choose Air Cooled Heat Exchangers Over Water Cooled Systems?
- Water Independence: No need for a continuous water supply or cooling towers.
- Environmental Compliance: Avoids chemical treatments and discharge issues associated with water cooling.
- Low Operating Costs: Less infrastructure and reduced utility bills.
- Long Service Life: Less corrosion and fouling compared to water-based systems.
- Ideal for Remote Areas: Perfect for industries operating in deserts, offshore rigs, or mountainous zones.
Where Are Air Cooled Heat Exchangers Used?
Air cooled heat exchangers are deployed across a wide spectrum of industries. Common applications include:
- Oil & Gas Refineries
- Petrochemical Plants
- Power Generation Units
- HVAC Systems
- Renewable Energy Plants
- Steel and Metal Processing
- Hydraulic Systems
- Compressors and Turbines
How Is an Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Constructed?
- Tube Bundle: Made of finned tubes (copper, aluminum, or stainless steel) to improve heat transfer.
- Fans: Axial or centrifugal fans move ambient air across the tubes. Powered by electric or hydraulic systems.
- Header Box: Ensures even fluid distribution and collection. Can be fixed, floating, or removable.
- Plenum Chamber: Guides air between the fan and tube bundles for uniform flow.
- Frame Structure: Steel or aluminum housing that supports the unit.
- Louvers and Dampers: Optional controls for airflow management and maintenance.
What Types of Air Cooled Heat Exchangers Exist?
- Forced Draft Type: Fans below the bundle push air upwards easier for maintenance.
- Induced Draft Type: Fans above the bundle pull air through provides uniform cooling.
- A-Frame or V-Type: Compact, efficient design suited for space constrained installations.
- Modular Units: Multiple units combined for larger capacity systems.
How to Select the Right Air Cooled Heat Exchanger?
- Type of Fluid: Consider corrosiveness, viscosity, and temperature sensitivity.
- Flow Rate and Temperature: Influences material choice and fan size.
- Site Conditions: Ambient temperature and humidity affect performance.
- Space Constraints: May require compact or modular options.
- Maintenance: Choose fixed or removable headers as needed.
- Power Source: Match to available electrical or hydraulic power.
What Are the Advantages of Air Cooled Heat Exchangers?
| Advantage |
Description |
| Water-Free Operation |
Ideal for dry or remote locations |
| Lower Environmental Impact |
No chemical discharge or water pollution |
| Easy Maintenance |
No water treatment or scaling issues |
| Flexible Installation |
Can be installed outdoors or on rooftops |
| Energy Efficient |
Fan speed can be optimized with VFDs |
| Scalable Design |
Multiple modules can be connected for higher capacity |
How to Maintain an Air Cooled Heat Exchanger?
- Regular Cleaning: Clean finned tubes to remove dust and debris.
- Fan Checks: Inspect blades and alignment regularly.
- Tube Inspection: Look for leaks, corrosion, or fouling.
- Lubrication: Keep motors and bearings well-lubricated.
- Temperature Monitoring: Check inlet/outlet temperatures for anomalies.
Define the Future of Air Cooled Heat Exchangers
- Smart Monitoring: Real-time tracking of temperature and fan performance.
- VFD Integration: Variable fan speeds based on demand.
- Eco Materials: Use of recyclable and anti-corrosive materials.
- Compact Designs: For tight urban or offshore installations.
What Are the Key Factors That Influence the Performance of Air Cooled Heat Exchangers?
- Ambient Air Temperature: Affects the cooling gradient and system performance.
- Airflow Rate: Sufficient and uniform airflow is critical for efficient heat transfer.
- Fin and Tube Material: Material choice impacts conductivity and durability.
- Fouling and Contamination: Dust/oil buildup reduces efficiency; regular cleaning is vital.
- Altitude and Air Density: Higher altitudes require compensation through design adjustments.
What Innovations Are Emerging in the Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Industry?
- Smart Exchangers: Sensors and IoT-enabled monitoring for predictive maintenance.
- Hybrid Cooling: Combining air and evaporative cooling for hotter climates.
- Noise Control: Low-noise blades and acoustic dampening features.
- Advanced Materials: Nanotech coatings and corrosion-resistant alloys.
How to Improve the Efficiency of Your Air Cooled Heat Exchanger?
- Clean fins and filters regularly.
- Maintain fan motor efficiency.
- Install VFDs to optimize fan performance.
- Use air guides to maintain airflow distribution.
- Conduct seasonal performance inspections.
Why Should You Consider Partnering with a Specialized Manufacturer?
Choosing a reputable manufacturer ensures quality and performance. Benefits include:
- Custom design per application needs
- CFD modeling and performance prediction
- Certified Material Testing (ASME, TEMA, API)
- Installation & commissioning support
- Lifecycle cost savings and ROI focus
Where to Buy Air Cooled Heat Exchangers?
If you're looking for reliable and efficient Air Cooled Heat Exchangers,
United Cooling Systems is a trusted name in the industry. With decades of experience, United Cooling Systems designs and manufactures high-performance ACHEs tailored to meet the demanding needs of various industrial sectors.
Why Buy from United Cooling Systems?
- Proven expertise in thermal engineering and process cooling
- Fully customized solutions to match your specific application
- Global supply network and responsive technical support
- State-of-the-art manufacturing with stringent quality control
- Eco-friendly designs focused on energy efficiency and zero water use
Whether your project involves petrochemicals, refineries, power plants, or manufacturing, United Cooling Systems delivers robust and efficient air-cooled solutions built to perform in extreme environments.
Get in Touch
An Air Cooled Heat Exchanger is more than just equipment it is a strategic investment in operational efficiency, environmental responsibility, and long-term savings. Selecting the right unit and manufacturer can have a lasting impact on your system's performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Air Cooled Heat Exchangers a Complete Alternative to Water Cooled Systems?
Not always. High-capacity systems may still require water cooling.
- Are air cooled heat exchangers suitable for mobile machinery?
Yes. Especially V-type units for mining and construction equipment.
- How energy efficient are these systems?
Very efficient, especially with VFD-controlled fan systems.
- How long does an ACHE last?
Typically 15 to 25 years with proper care.
- What industries benefit most?
Oil & gas, power, petrochemical, and heavy industries.


